Angiogenin ELISA Kits
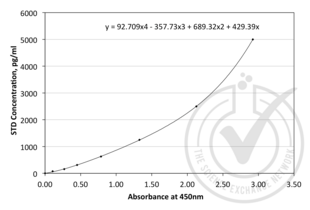
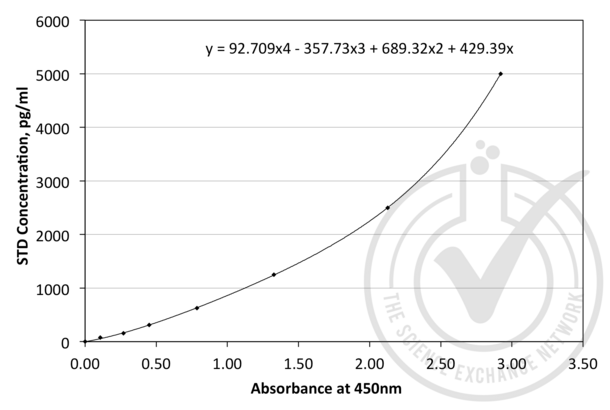 ANG ELISA Kit (ABIN365222)
ANG ELISA Kit (ABIN365222)
ANG Reaktivität: Human Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA 15.6-1000 pg/mL Cell Culture Supernatant, Plasma, Serum, Tissue Homogenate, Urine
ANG Reaktivität: Maus Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA 0.31 ng/mL - 20 ng/mL Plasma, Serum
ANG Reaktivität: Human Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA 31.2 pg/mL - 2000 pg/mL Cell Culture Supernatant, Cell Lysate, Plasma, Serum, Tissue Homogenate
Angiogenin ELISA Kits nach Reaktivität
Hier sind Angiogenin ELISA Kits für eine Vielzahl von Species wie anti-Human Angiogenin, anti-Pig Angiogenin, anti-Chicken Angiogenin zu finden. Die unten aufgeführten Species gehören zu den verfügbaren Arten. Klicken Sie auf einen Link, um zu den entsprechenden Produkten zu gelangen.
Angiogenin ELISA Kits nach Detektionsmethode
Hier sind Angiogenin ELISA Kits mit einem spezifischen Detektionsmethode zu finden. Die hier aufgeführten Detektionsmethode sind einige der verfügbaren. Ein Klick auf den entsprechenden Link führt zu den Produkten.
Angiogenin ELISA Kits nach Analytische Methode
Hier sind Angiogenin ELISA Kits mit einem spezifischen Analytische Methode zu finden. Die hier aufgeführten Analytische Methode sind einige der verfügbaren. Ein Klick auf den entsprechenden Link führt zu den Produkten.
Angiogenin ELISA Kits nach Methodentyp
Hier sind Angiogenin ELISA Kits mit einem spezifischen Methodentyp zu finden. Die hier aufgeführten Methodentyp sind einige der verfügbaren. Ein Klick auf den entsprechenden Link führt zu den Produkten.
Angiogenin ELISA Kits nach Probe
Hier sind Angiogenin ELISA Kits mit einem spezifischen Probe zu finden. Die hier aufgeführten Probe sind einige der verfügbaren. Ein Klick auf den entsprechenden Link führt zu den Produkten.
Angiogenin ELISA Kits nach Bindungsspezifität
Hier sind Angiogenin ELISA Kits mit einem bestimmten Epitop aufgelistet. Die unten aufgeführten Epitope gehören zu den verfügbaren Epitopen. Klicken Sie auf einen Link, um zu den entsprechenden Produkten zu gelangen.
Häufig verwendete Angiogenin ELISA Kits
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (4)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
Aktuelle Publikationen für unsere Angiogenin ELISA Kits
: "The VE-PTP Inhibitor AKB-9778 Improves Antitumor Activity and Diminishes the Toxicity of Interleukin 2 (IL-2) Administration." in: Journal of immunotherapy (Hagerstown, Md. : 1997), Vol. 42, Issue 7, pp. 237-243, (2020) (PubMed).: "Angiogenin/Ribonuclease 5 Is an EGFR Ligand and a Serum Biomarker for Erlotinib Sensitivity in Pancreatic Cancer." in: Cancer cell, Vol. 33, Issue 4, pp. 752-769.e8, (2019) (PubMed).
: "Serum Angiopoietin Levels are Different in Acute and Chronic Myeloid Neoplasms: Angiopoietins do not only Regulate Tumor Angiogenesis." in: Indian journal of hematology & blood transfusion : an official journal of Indian Society of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Vol. 32, Issue 2, pp. 162-7, (2016) (PubMed).
: "Angiotensin II as a morphogenic cytokine stimulating fibrogenesis of human tenon's capsule fibroblasts." in: Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, Vol. 56, Issue 2, pp. 855-64, (2015) (PubMed).
: "38" in: , Vol. 1363, Issue Nucleic acids research, pp. 28-39, (1991)
: "Radiation-induced angiogenic signaling pathway in endothelial cells obtained from normal and cancer tissue of human breast." in: Oncogene, Vol. 33, Issue 10, pp. 1229-38, (2014) (PubMed).
: "Angiogenic properties of dehydrated human amnion/chorion allografts: therapeutic potential for soft tissue repair and regeneration." in: Vascular cell, Vol. 6, pp. 10, (2014) (PubMed).
: "Antiangiogenic treatment diminishes renal injury and dysfunction via regulation of local AKT in early experimental diabetes." in: PLoS ONE, Vol. 9, Issue 4, pp. e96117, (2014) (PubMed).
: "Clinical outcome, proteome kinetics and angiogenic factors in serum after thermoablation of colorectal liver metastases." in: BMC cancer, Vol. 13, pp. 266, (2014) (PubMed).
: "Influence of thyroid state on cardiac and renal capillary density and glomerular morphology in rats." in: The Journal of endocrinology, Vol. 216, Issue 1, pp. 43-51, (2013) (PubMed).
Aliase für Angiogenin ELISA Kits
angiogenin (ANG) ELISA Kitsangiogenin, ribonuclease, RNase A family, 5 (Ang) ELISA Kits
angiogenin, ribonuclease, RNase A family, 5 (ANG) ELISA Kits
angiogenin (Ang) ELISA Kits
ribonuclease A family member k6 (RNASE6) ELISA Kits
AI385586 ELISA Kits
ALS9 ELISA Kits
ANG ELISA Kits
Ang1 ELISA Kits
ANG1 ELISA Kits
HEL168 ELISA Kits
RNASE4 ELISA Kits
RNASE5 ELISA Kits
Rnase5 ELISA Kits
Rnase5a ELISA Kits
Haben Sie etwas anderes gesucht?
- ANG2 ELISA Kits
- Androstenedione ELISA Kits
- Androgen Receptor ELISA Kits
- Ancient Ubiquitous Protein 1 ELISA Kits
- ANAPC2 ELISA Kits
- Amylin/DAP ELISA Kits
- Amylase, alpha ELISA Kits
- Amylase ELISA Kits
- AMY2A ELISA Kits
- AMY2 ELISA Kits
- AMY1A ELISA Kits
- AMPK alpha ELISA Kits
- Amphiregulin ELISA Kits
- Amphiphysin ELISA Kits
- AMPD2 ELISA Kits
- AMOTL2 ELISA Kits
- AMOTL1 ELISA Kits
- AMN ELISA Kits
- Aminomethyltransferase ELISA Kits
- Aminoacylase 1 ELISA Kits
- Angiomotin ELISA Kits
- Angiopoietin 1 ELISA Kits
- Angiopoietin 2 ELISA Kits
- Angiopoietin 4 ELISA Kits
- Angiostatin ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin 1-7 ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme 1 ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin II ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin II Receptor, Type 1 ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin II Receptor, Type 1 Antibody ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor ELISA Kits
- Angiotensin III ELISA Kits
- ANGPTL1 ELISA Kits
- ANGPTL2 ELISA Kits
- ANGPTL3 ELISA Kits
- ANGPTL4 ELISA Kits
- ANGPTL6 ELISA Kits
- ANGPTL7 ELISA Kits
- Anillin ELISA Kits
- ANK2 ELISA Kits




